Where do risk assets come from when the Bank of Japan sends a progressive signal from the Eagles
By Zhou, ChainCatcher
THE CENTRAL BANK OF JAPAN (BOJ), AT ITS MONETARY POLICY CONFERENCE, WHICH ENDED ON 19 DECEMBER 2025, DECIDED TO INCREASE THE POLICY INTEREST RATE BY 25 BASIS POINTS, FROM 0.5 PER CENT TO 0.75 PER CENT. THIS WAS THE SECOND INCREASE IN INTEREST RATES SINCE JANUARY THIS YEAR, WITH INTEREST RATES AT A RECORD LEVEL SINCE 1995。
the resolution was adopted by a full vote of 9:0 and is fully in line with market expectations. the 50 economists previously interviewed had unanimously predicted the increase, which was the first time that &ldquo had appeared in the governor ' s field and in the men ' s office; ” and the expected increase。
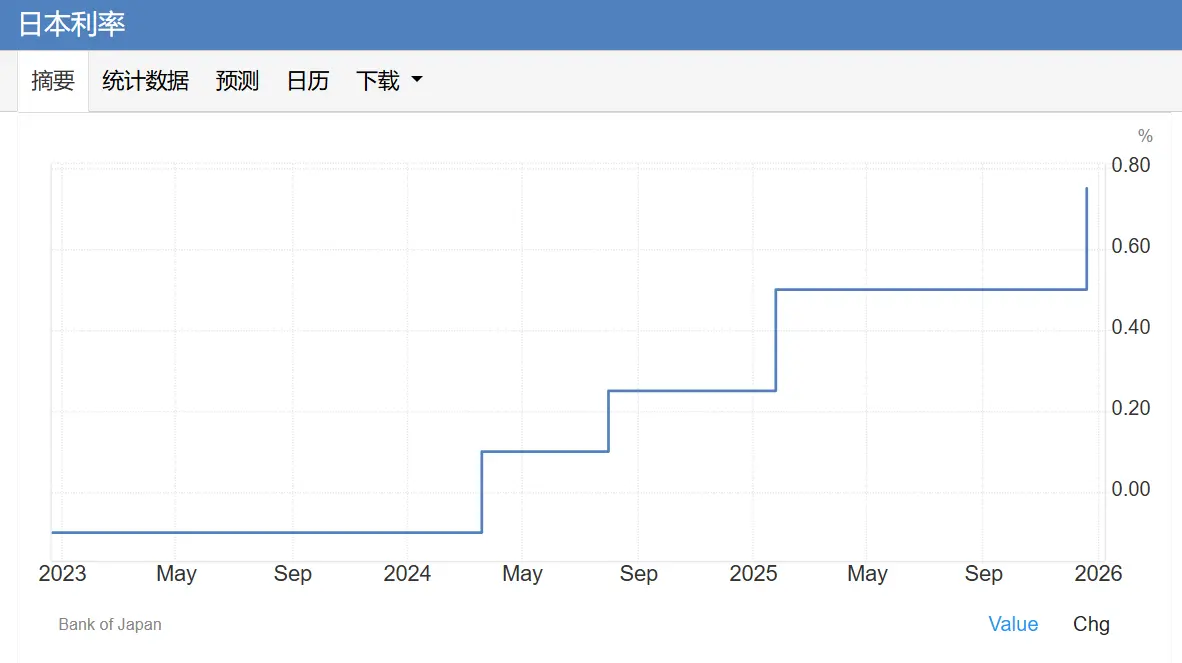
In a press conference, the Governor of the Central Bank of Japan, Shida-san, stated that short-term interest rates at 30 years' high did not mean anything special, and that the effects of changes in interest rates would be closely monitored by the authorities. He stated that there was still a distance between the floors of the neutral interest zone and that the market should not expect to give a precise range of neutral interest rates in the short term. The pace of adjustment of subsequent monetary support policies will depend on economic growth, price performance and the financial market environment at that time。
It was emphasized that the assessment of economic prospects, price risks and the likelihood of achieving targets would be updated at each meeting and that decisions would be made accordingly. He acknowledged that the estimates of neutral interest rates in Japan were broad enough to be accurate and that it was necessary to observe the actual feedback from the economy and prices on each interest rate change. There is a real possibility of an increase in interest rates if wage increases continue to flow to prices。
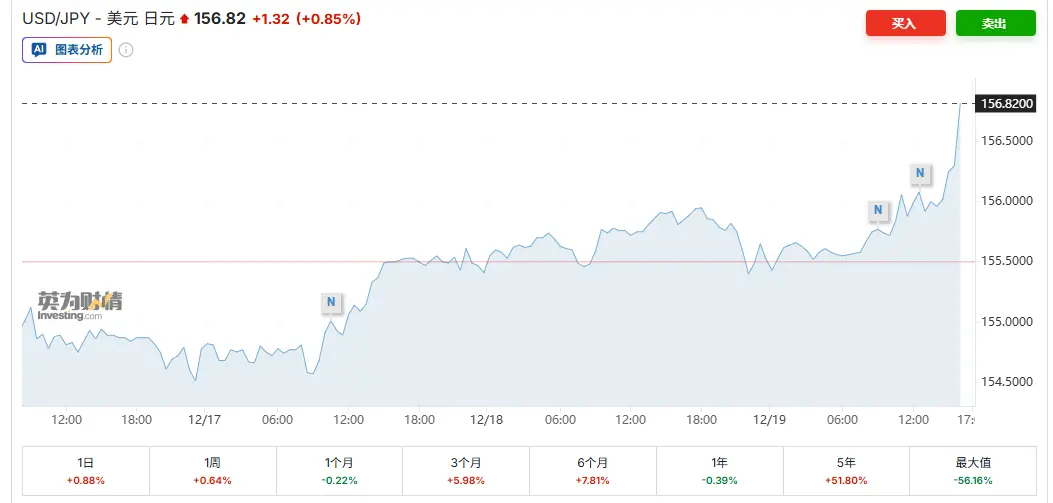
The reaction of the capital markets was relatively calm: the exchange rate of the United States dollar to the Japanese yen increased slightly by 0.3 per cent to 156.06; Japan, 30 years old, the rate of return on the national debt rose slightly by 1 basis point to 3.385 per cent; the number rose by 1.5 per cent on the 225 index board; 49,737.92 points were reported; the bitcoin rose by $87,000, representing an increase of 1.6 per cent in the day. For the time being, the risk assets as a whole did not show significant pressure to sell。
LOOKING BACK AT THE FUNDAMENTALS, JAPAN'S INTEREST RATE HIKE HAS RECEIVED SUFFICIENT DATA SUPPORT. ITS CORE CPI INCREASED BY 3.0 PER CENT IN NOVEMBER IN LINE WITH EXPECTATIONS, WITH INFLATIONARY PRESSURES REMAINING STRONG AND 44 CONSECUTIVE MONTHS ABOVE THE POLICY TARGET OF 2 PER CENT; IN ADDITION, WAGE GROWTH HAS BEEN STRONG, CONFIDENCE IN LARGE MANUFACTURING HAS RISEN TO FOUR YEARS, AND EVEN IN THE FACE OF UNITED STATES TARIFF PRESSURES, THE ADJUSTMENT OF THE ENTERPRISE SUPPLY CHAIN HAS SHOWN CONSIDERABLE RESILIENCE, WITH SHOCKS BELOW EXPECTATIONS。
meanwhile, japan’s major trade unions in the upcoming & ldquo; chun do & rdquo; have set a pay-up target equal to last year’s, which shows that the most significant pay-up in decades has been achieved last year, indicating that the drive for salary growth is still continuing。
Overall, this small interest rate increase marks Japan’s official departure from a long period of ultra-laxity or will be an important turning point in global venture asset liquidity at the end of the year。
Has the market fully digested expectations
The current market pricing shows that the Bank of Japan is likely to raise interest rates again in June or July. In the view of Morgan Chase private banks, interest rate hikes have had a limited boost to the yen due to adequate market pricing. The interest rate is expected to increase once more to 1 per cent in 2026, the United States dollar against the Japanese yen base will remain at a high level near 150, and negative spreads and fiscal risks will continue to limit the value-added potential of the yen as potential defensive zones。
Some analysts, however, questioned that the timetable was too radical, arguing that October 2026 was a more realistic window period, which allowed enough room to assess the impact of rising borrowing costs on business finance, bank credit and household consumption. At that time, the outcome of the spring salary negotiations and the Japanese yen exchange rate would be the core assessment indicator。
moreover, morgan stanley expects that after the 25bp hike, the central bank of japan will continue to emphasize the liberal properties of the policy environment, with interest rates below the neutral level. future austerity paths will be gradual and highly dependent on data and will not foresee radical routes。
InvestingLive Analyst Eamon Sheridan argues that since real interest rates are still negative and the policy as a whole is broad, the next increase is expected to be at the earliest in mid-2026 to observe the actual penetration of borrowing costs into the economy。
japan ' s ultra-low interest rate environment has long provided a hugely cheap liquidity to the global market. through “ yen arbitrage & rdquo; investors borrow japanese yen at low cost and invest in high-yield assets such as united states shares, encrypted currency, etc. the size of this mechanism has been an important support for the venture capital markets of the past years。
ALTHOUGH THE LATEST TIC DATA INDICATE THAT PUBLIC DEBT HAS NOT YET RETURNED TO THE US DEBT MARKET ON A LARGE SCALE (TO $1.2 TRILLION IN OCTOBER), THIS TREND HAS EITHER EMERGED AS JAPAN’S LOCAL DEBT (JGB) HAS INCREASED ITS ATTRACTIVENESS, THUS PUSHING US DEBT YIELDS AND GLOBAL DOLLAR FINANCING COSTS UPWARDS, STIFLING RISKY ASSETS。
Most mainstream central banks are currently in a declining interest rate cycle, while the central bank of Japan is divided by counter-market interest rate hikes. This contrast is highly likely to trigger arbitrage silos, while a secure market with high leverage and 24-hour trading characteristics is usually the first to feel a liquidity shock。
Macro analysts had warned that bitcoin would be at risk of looking back at $70,000 if the Bank of Japan raised interest on December 19. Historical data show that there has been a significant return on bitcoin since the last three hikes, usually falling 20-30 per cent in 4-6 weeks. For example, in March 2024, it fell by 23 per cent, in July by 26 per cent, and in January 2025 by 31 per cent, after the market was very worried that the increase would be repeated。
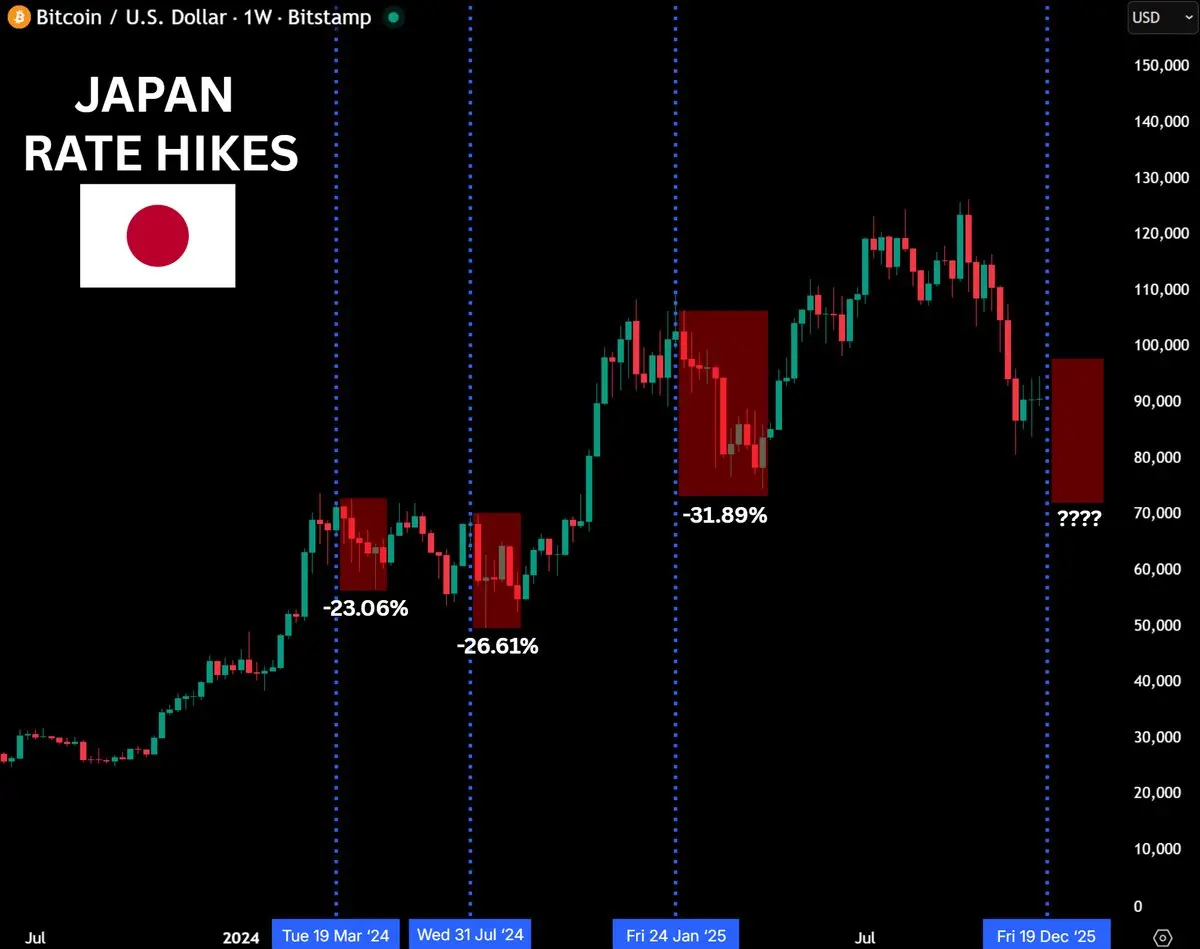
Warningers argue that Japan ' s interest rate hike remains one of the largest variables in current asset pricing, its role in global capital markets is underestimated and policy shifts can trigger widespread deleveraging。
The neutral view, on the other hand, is that the simple reason for the historical decline is that Japan’s interest rate hike is too one-sided, and that the interest rate hike is expected to be extremely adequate (the encryption market has been retroverted earlier in the week), and that most panic has been factored into prices, and analysts say that the market is more afraid of uncertainty than austerity itself。
IT IS WORTH MENTIONING THAT, ACCORDING TO BLOOMBERG, THE BANK OF JAPAN WILL START THE PROGRESSIVE LIQUIDATION OF ETF ASSETS AT THE EARLIEST POSSIBLE DATE IN JANUARY 2026. AS AT THE END OF SEPTEMBER, ITS ETF WAREHOUSE HAD A MARKET VALUE OF APPROXIMATELY 83 TRILLION YEN. IF, IN 2026, WITH MULTIPLE INTEREST RATES, BONDS ARE SOLD OR WILL ACCELERATE, THE CONTINUED DECOMPOSITION OF THE YEN ARBITRAGE WILL TRIGGER THE SALE OF RISKY ASSETS AND THE RETURN OF THE YEN, WITH A PROFOUND IMPACT ON THE STOCK MARKET AND ENCRYPTED CURRENCIES。
Click to find ChainCatcher in position
